Tobacco Smoking Cessation: How to Promote Healthy Heart Care?

Smoking tobacco is one of the major causes of heart and blood vessel diseases worldwide. Even with all the warnings and health campaigns, more than a billion people still smoke.
Every year, millions of those smokers face early deaths from heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems caused by tobacco use.
The World Health Organization says smoking causes almost 10% of all heart-related deaths globally. This makes quitting smoking one of the most important steps you can take to protect your heart.
Smoking harms your heart and blood vessels in many ways. It can cause narrowing of arteries, increase the chance of blood clots, raise bad cholesterol, and cause inflammation inside your blood vessels. These changes make heart attacks and strokes much more likely.
But the good news is that quitting smoking cuts these risks dramatically. The body starts to heal right away when you stop. Still, quitting is not easy because nicotine is very addictive, and smoking often becomes a hard habit to break.
Advances in wearable technology with simple lifestyle changes, offer new ways to support quitting. These tools track your body’s signals and give personalized feedback to help manage cravings, reduce stress, and keep you motivated.
In this blog post, we’ll look at how smoking is harmful to your heart health and why quitting is so important. You will learn how AI-powered wearables and lifestyle changes can help you in tobacco smoking cessation.
How Smoking Harms Your Heart and Blood Vessels?
To understand why smoking is so bad for your heart, let’s look at what happens inside your body when you light up.
Damage to the Blood Vessel Lining
Inside your blood vessels is a thin layer of cells called the endothelium. This lining helps keep your vessels flexible, controls blood flow, and stops clots from forming when they’re not needed.
When you smoke, chemicals like nicotine and carbon monoxide enter your bloodstream. These chemicals damage the endothelium by causing inflammation and oxidative stress, which means your body produces harmful molecules called free radicals.
One important effect of smoking is the reduction of nitric oxide. This molecule helps your vessels relax and stay open. With less nitric oxide, your blood vessels become narrow and stiff. This makes it harder for blood to flow and sets the stage for plaque buildup, also known as atherosclerosis.
Inflammation and Plaque Formation
Smoking triggers chronic inflammation. Your immune system reacts to the damage by sending cells to repair it, but this response can go overboard. The inflammation causes immune cells to collect in your arteries and take up fats, forming plaques.
These plaques narrow your arteries and can rupture suddenly. When they rupture, a blood clot can form quickly and block blood flow, causing a heart attack or stroke.
Thicker Blood and Clot Risks
Nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco increase the stickiness of your blood platelets. Platelets are cells that help blood clot to stop bleeding. When they become too active, clots can form inside your arteries, which is dangerous. Smoking also raises fibrinogen, a protein that helps clots form.
At the same time, it lowers the activity of the system that breaks down clots. This imbalance means your blood is more likely to clot when it shouldn’t, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Unhealthy Cholesterol Levels
Smoking affects your blood fats. It raises levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), the “bad” cholesterol, and triglycerides, while lowering high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the “good” cholesterol. Such a mix accelerates the formation of plaques in your arteries.
Nicotine also stimulates your nervous system to release stress hormones like adrenaline, which raise blood sugar and free fatty acids in your blood. These changes make your body less sensitive to insulin, increasing the risk of diabetes, which is another risk factor for heart disease.
Why Quitting Smoking Protects Your Heart Fast?
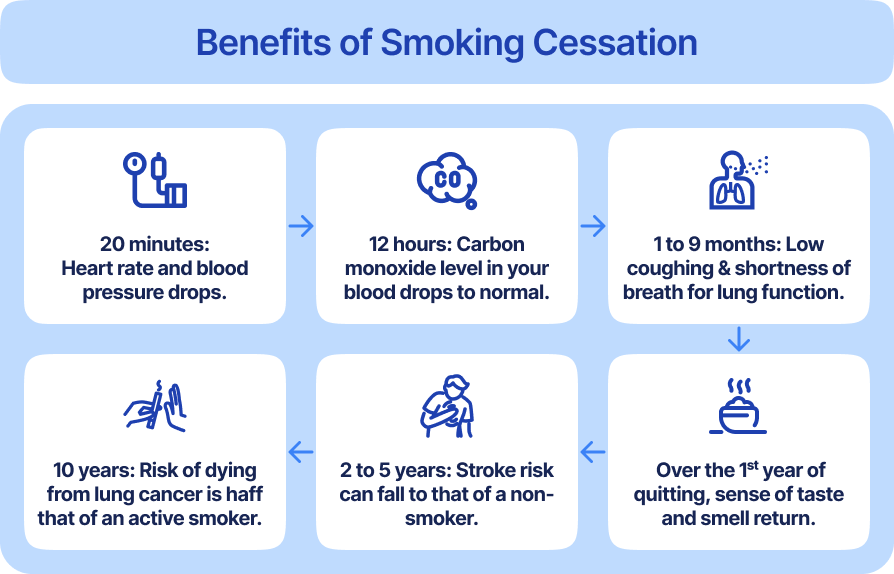
The moment you stop smoking, your body starts to repair itself. The changes happen quickly and keep improving with time:
- Within 20 minutes, your heart rate and blood pressure begin to drop towards normal.
- Within 12 hours, the carbon monoxide level in your blood returns to normal, improving oxygen delivery.
- Within weeks, the blood vessels start working better, and inflammation goes down.
- Within one year, your risk of coronary heart disease falls by about half.
- Within 5 to 15 years, your risk of stroke and heart attack drops to levels similar to someone who never smoked.
These improvements show “it’s never too late to quit”. Even if you’ve smoked for decades, your heart health can get better with time.
How Wearable Technology Helps You Quit Smoking?
Quitting smoking usually involves counseling, medications, or nicotine replacement therapies. These methods help many people but often don’t fit every lifestyle or provide ongoing motivation.
AI-powered wearables are devices you wear on your wrist or body. They monitor things like your heart rate, stress levels, and sleep quality. They can spot signs of cravings or stress before you even realize it.
When they detect these signs, they offer help right away—whether that’s a reminder to breathe deeply, a suggestion to move around, or encouraging words to keep going.
Here are some key ways AI-powered wearables support quitting:
- Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability (HRV): HRV shows how well your body handles stress. Lower HRV can mean you’re stressed or struggling. Wearables track this and signal when you need to calm down.
- Galvanic Skin Response (GSR): This measures how much you sweat, which changes with stress or anxiety.
- Skin Temperature: Withdrawal symptoms can change your skin temperature, which wearables can detect.
- Physical Activity: Exercise helps manage cravings and mood, so tracking movement is useful.
- Sleep Quality: Poor sleep increases relapse risk. Wearables monitor sleep and suggest improvements.
Wearable devices often connect to smartphone apps. These apps offer personalized advice, track your progress, and even connect you to quit coaches or support groups. Some programs allow healthcare providers to see your data remotely, so they can adjust your treatment and support you better.
Simple Lifestyle Changes That Make a Big Difference in Smoking Cessation

Beyond wearables, smoking cessation also requires real lifestyle changes. Here are some habits that help:
1. Exercise
Physical activity helps in many ways. It lowers withdrawal symptoms like anxiety and irritability. Exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood. It also strengthens your heart and helps prevent weight gain after quitting. Aim for at least 30 minutes of aerobic exercise like walking, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week.
2. Healthy Eating
A diet full of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains provides antioxidants that fight damage caused by smoking. Vitamins like C and E help reduce inflammation. Avoid too much caffeine and alcohol, as they can trigger cravings or weaken your willpower.
3. Stress Management
Stress is a major cause of relapse. Techniques like deep breathing, mindfulness, and meditation help reduce stress and improve focus. Many wearable apps offer guided sessions to practice these methods exactly when you need them.
4. Better Sleep
Sleep is crucial for controlling cravings and making good decisions. Poor sleep makes you more likely to relapse. Try to keep a regular sleep schedule, avoid screens before bedtime, and create a calm environment to rest.
5. Avoiding Triggers
Changing your daily routine, avoiding places or people that make you want to smoke, and building a support network all help reduce exposure to smoking cues.
Challenges and Future Possibilities for Wearables and Smoking Cessation
While wearable technology is promising, it still has challenges:
- Sensor Accuracy: Devices can sometimes give false readings, especially when worn differently or affected by the environment. Improving sensors and the AI that interprets data is ongoing work.
- Privacy and Security: Your health data is private and sensitive. Companies must protect it with strong security and clear policies to earn your trust.
- Staying Motivated: Using wearables and apps regularly is key to success. Features like reminders, gamification, and personalized feedback help keep users engaged.
- Clinical Integration: Combining AI-powered wearables with medical treatment and counseling offers the best results. Doctors can use the data to better guide patients.
Research is also exploring new ways to detect smoking, like sensors that measure chemicals in sweat or breath. Making these technologies affordable and accessible will help more people quit smoking worldwide.
Final Thoughts
Smoking causes serious damage to your heart and blood vessels. It does this through inflammation, narrowing of arteries, thicker blood, and unhealthy cholesterol. Quitting smoking cuts your risk of heart disease quickly and continues to improve your health over the years.
Wearable devices act as an additional layer of support by monitoring your body in real-time and helping manage cravings and stress. When combined with lifestyle changes like exercise, good nutrition, stress control, and better sleep, they increase your chances of quitting successfully.
If you or someone you care about wants to quit smoking, Helius Wellness recommends using these tools along with healthy habits can protect the heart and lead to a healthier, smoke-free life.
Popular Blogs

Agentic AI-Driven Healthcare Revolution
Agentic AI in healthcare for personalised care and real-time decisions.

Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A New Approach t...
Chronic disease care with AI wearables, remote monitoring, and more.

AI and Hallucinations in Healthcare Field: A New Fronti...
Know how AI supports the detection and treatment of hallucinations.
